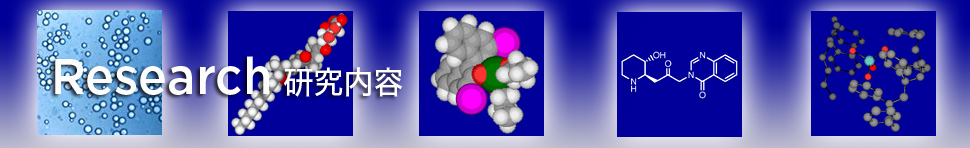
Selective C-H Functionalization via Single Electron Transfer Process (SET)
New methodologies in cross-coupling reactions using carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bonds as substrates is of great interest due to the challenges associated with C-H bond activation and the potential to streamline synthesis by the elimination of pre-activated coupling reagents. The purpose of this research is to utilize the power of single electron transfer (SET) processes to facilitate selective C-H bond functionalization of amines.
Topics
- Metal-Free Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling Reaction of Tertiary Amines
- Cooperative Catalytic System for the Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling Reaction of Tertiary Amines
- Metal Antimonates as Bifunctional Catalysts for Oxidative Coupling Reactions
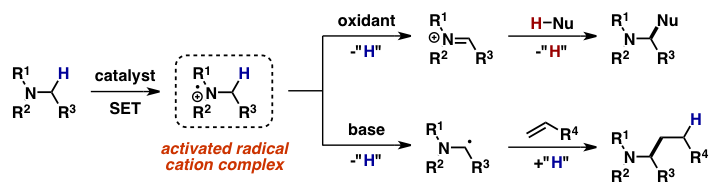
Metal-Free Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling Reaction of Tertiary Amines
Comment
By utilizing catalytic amounts of sulfuryl chloride (SO2Cl2), a mild protocol for the metal-free cross-dehydrogenative coupling(CDC) reaction of tertiary amines under aerobic conditions was developed. Due to the nature of SO2Cl2, it is believed that this reagent acts as a radical initiator to induce the metal-free CDC reaction via a radical-initiated autoxidation mechanism.
Access to paper
- Sulfuryl Chloride as an Efficient Initiator for the Metal-Free Aerobic Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling Reaction of Tertiary Amines,
- A. Tanoue, W.-J. Yoo, S. Kobayashi,
- Org. Lett., 16, 2346-2349 (2014). DOI: 10.1021/ol500661t
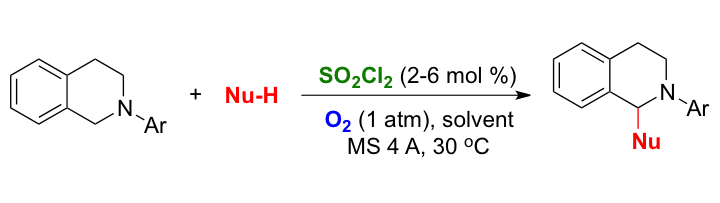
Cooperative Catalytic System for the Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling Reaction of Tertiary Amines

Comment
A cooperative catalytic system between hexachlorantimonate anion and N-hydroxyphthalimide (NHPI) was developed for the aerobic cross-dehydrogenative coupling (CDC) reaction of N-aryl tetrahydroisoquinolines.
Access to paper
- Antimony/N-Hydroxyphthalimide as a Catalyst System for Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling Reactions under Aerobic Conditions,
- A. Tanoue, W.-J. Yoo, S. Kobayashi,
- Adv. Synth. Catal., 355, 269-273 (2013). DOI: 10.1002/adsc.201200999
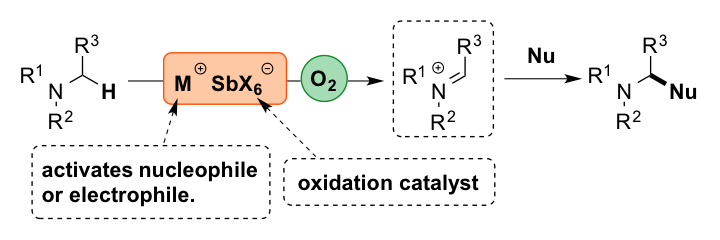
Metal Antimonates as Bifunctional Catalysts for Oxidative Coupling Reactions
Comment
Based on our previous discovery of an antimonate anion as an effective catalyst for the cross-dehydrogenative (CDC) reaction of N-aryl tetrahydroisoquinolines, a bifunctional metal antimonate catalytic system was designed. It was found that a well-defined zinc antimonate salt was found to be an effective catalyst for the α-allylation of glycine derivatives.
Access to papers
- Zinc(II) Hexachloroantimonate-Catalyzed Oxidative Allylation of Glycine Derivatives,
- W.-J. Yoo, A. Tanoue, S. Kobayashi,
- Asian J. Org. Chem., 3, 1066-1069 (2014). DOI: 10.1021/ajoc.201402108